
Hexadecimal numbers are often represented by the value preceded by 0x (e.g., 0x73) to distinguish between decimal and hexadecimal values in documentation. For example, in the table, the binary value 0000 1010 is shown in hexadecimal as 0A. When using hexadecimal, leading zeroes are always displayed to complete the 8-bit representation. Selected Decimal, Binary, and Hexadecimal Equivalents Decimal, Binary, and Hexadecimal Equivalents Given that 8 bits (one byte) is a common binary grouping, binary 00000000 to 11111111 can be represented in hexadecimal as the range 00 to FF, as shown in the next figure. Decimal and Binary Equivalents of 0 to F Hexadecimal Decimal and Binary Equivalents The figure compares the equivalent decimal and hexadecimal values for binary 0000 to 1111.
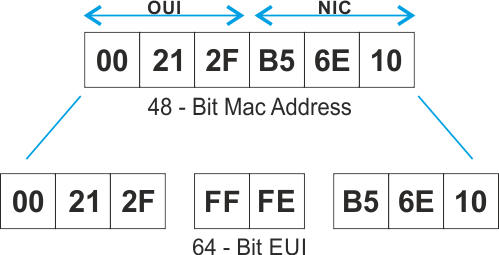
Therefore, a 48-bit Ethernet MAC address can be expressed using only 12 hexadecimal values. Hexadecimal is used to identify an Ethernet address because a single hexadecimal digit represents four binary bits. The hexadecimal numbering system uses the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F.Īn Ethernet MAC address consists of a 48-bit binary value. To understand hexadecimal, you must first be very familiar with binary and decimal. IPv6 addresses and Ethernet addresses are represented using the hexadecimal base sixteen number system. In networking, IPv4 addresses are represented using the decimal base ten number system and the binary base 2 number system. Lab – View Network Device MAC Addresses.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
